Global air circulation Notes for Grade 12 Here are some key points on global air circulation that you might find useful for Grade 12 studies:
Here’s an overview of global air circulation:
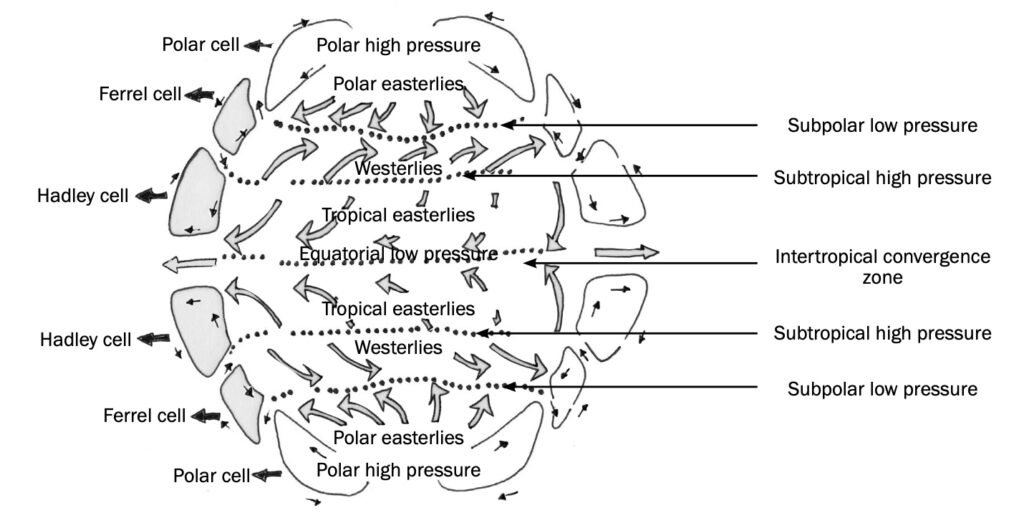
1. Hadley Cell:
- Location: Near the equator (0-30 degrees latitude).
- Description: The Sun’s intense heat at the equator causes air to rise, creating a low-pressure zone. As the air rises, it cools and releases moisture, forming clouds and precipitation. The rising air moves towards the poles aloft, creating the Hadley cell.
2. Ferrel Cell:
- Location: 30-60 degrees latitude in both hemispheres.
- Description: At these latitudes, the descending air from the Hadley cell creates high pressure. This air moves towards the poles near the surface. The Coriolis effect deflects this air, creating the westerlies (prevailing winds from the west).
3. Polar Cell:
- Location: Polar regions (60-90 degrees latitude).
- Description: Near the poles, cold air descends, creating a polar high-pressure zone. This air moves towards lower latitudes along the surface, creating the polar easterlies.
4. Coriolis Effect:
- Description: The rotation of the Earth causes moving air or water to be deflected to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. This effect influences the direction of global winds and ocean currents.
5. Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ):
- Location: Near the equator.
- Description: The meeting point of trade winds from the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It is characterized by low pressure, rising air, and frequent precipitation.
6. Trade Winds:
- Location: Between the equator and 30 degrees latitude.
- Description: Prevailing easterly winds in the tropics that move from east to west.
7. Westerlies:
- Location: Between 30 and 60 degrees latitude.
- Description: Prevailing winds from the west, moving from west to east.
8. Polar Easterlies:
- Location: Near the poles.
- Description: Cold easterly winds that blow from the polar high-pressure areas towards lower latitudes.
9. Monsoons:
- Description: Seasonal reversal of wind patterns, often associated with large-scale land-sea temperature differences. For example, the Indian subcontinent experiences a monsoon with a shift in wind direction between summer and winter.
Winds related to global air circulation
There are three global wind systems that are related to the global circulation:
- The tropical easterlies
- The westerlies
- The polar easterlies
What causes the circulation of air in the atmosphere
A force called Coriolis force causes global winds to move to the left in the southern hemisphere and to the right in the northern hemisphere. The tri-cellular arrangement, the pressure belts and the global winds together form the global air circulation.
The global air circulation diagram
Below is the global air circulation diagram
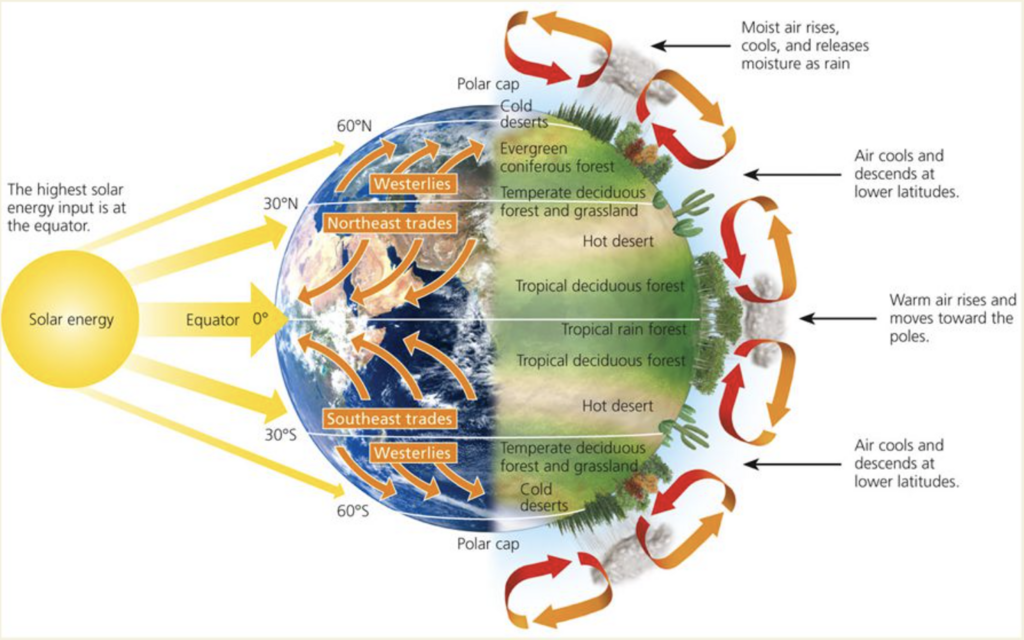
What are the 3 types of atmospheric circulation cells called?
The 3 types of atmospheric circulation cells called:
- Polar cell – The smallest and weakest cells are the Polar cells, which extend from between 60 and 70 degrees north and south, to the poles.
- Ferrel cell – Ferrel cell refers to a model that belongs to the mid-latitude region of the Earth’s wind flow
- Hadley cell – low-latitude overturning circulations that have air rising at the equator and air sinking at roughly 30° latitude.

Understanding global air circulation is crucial for comprehending weather patterns, climate zones, and the distribution of heat and moisture around the planet. It plays a significant role in shaping regional climates and weather events.