While the circular flow diagram is a useful tool for illustrating basic economic relationships, it is indeed a simplified representation and may not fully capture the complexities of the real-world economy.
The circular flow is a theoretical model that illustrates how money, goods, and services flow through an economy. The model depicts households, firms, and the government interacting in a continuous cycle of production, consumption, and exchange.
Reasons Why the Circular Flow is not an Accurate Reflection of Economic Reality
While the circular flow is a useful tool for understanding basic economic concepts, it is not an accurate reflection of economic reality. Here are the main reasons why circular flow is not an accurate reflection of economic reality:
- Firstly, the circular flow assumes that all households are the same, and all firms are the same. However, in reality, households and firms differ in their size, wealth, and economic power. Some households earn more money than others, and some firms have more resources and influence than others. This means that the interactions between households and firms are not always equal and can be influenced by factors such as wealth, power, and market concentration.
- Secondly, the circular flow assumes that there is no international trade, which is not an accurate reflection of the global economy. In reality, most economies are interconnected through international trade, and the circular flow model does not account for the flow of goods, services, and money between countries. This is particularly relevant for emerging economies that are increasingly dependent on global trade and investment.
- Thirdly, the circular flow model assumes that there is no government intervention, which is not an accurate reflection of modern economies. In reality, governments play an important role in regulating and stimulating economic activity through policies such as taxation, subsidies, and monetary policy. These policies can have a significant impact on the flow of money and resources in an economy and can distort the circular flow model.
- Lastly, the circular flow model assumes that all economic agents act rationally and in their own self-interest, which is not an accurate reflection of human behavior. In reality, people and firms often make decisions based on emotions, biases, and social norms. This means that the circular flow model may not account for the impact of these non-rational factors on economic behavior and decision-making.
While the circular flow model is a useful tool for understanding basic economic concepts, it is not an accurate reflection of economic reality. To better understand the complexities of modern economies, it is important to consider other factors that influence the flow of money, goods, and services, such as international trade, government intervention, and non-rational behavior.
Video Lesson: The Circular Flow Model of a Market Economy
Understanding the Circular Economy: The circular flow model demonstrates how money moves through society. Money flows from producers to workers as wages and flows back to producers as payment for products. In short, an economy is an endless circular flow of money.
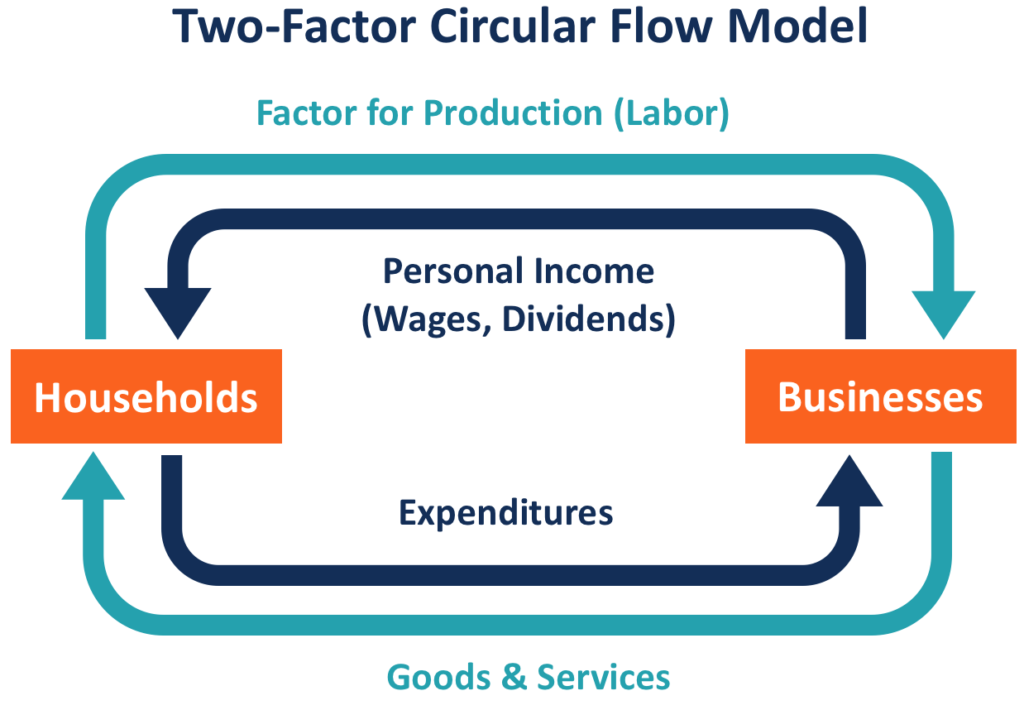
For the circular flow economic model to be the true reflection of the economy, it will have to incorporate the government, financial institutions, and the foreign sector.